Azure Storage Account
Radix supports mounting Azure storage account blob containers with the blobFuse2 volume type in radixconfig.yaml, using the blob-csi-driver.
General Settings
The only required settings in a blobFuse2 configuration are container and useAdsl.
container defines the name of the container in the Azure storage account to be mounted into the directory defined in path.
useAdls is a flag that defines if the storage account is hierarchical namespace enabled or not.
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
container: images
useAdls: true
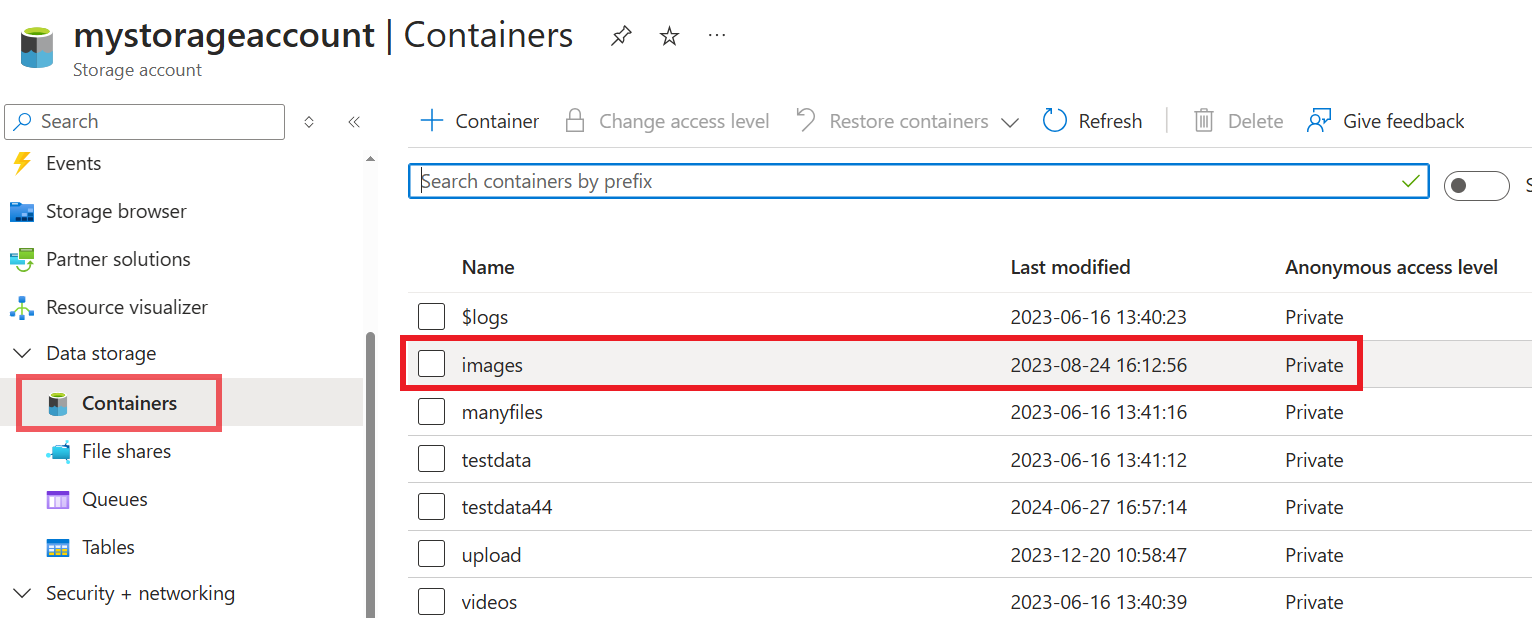
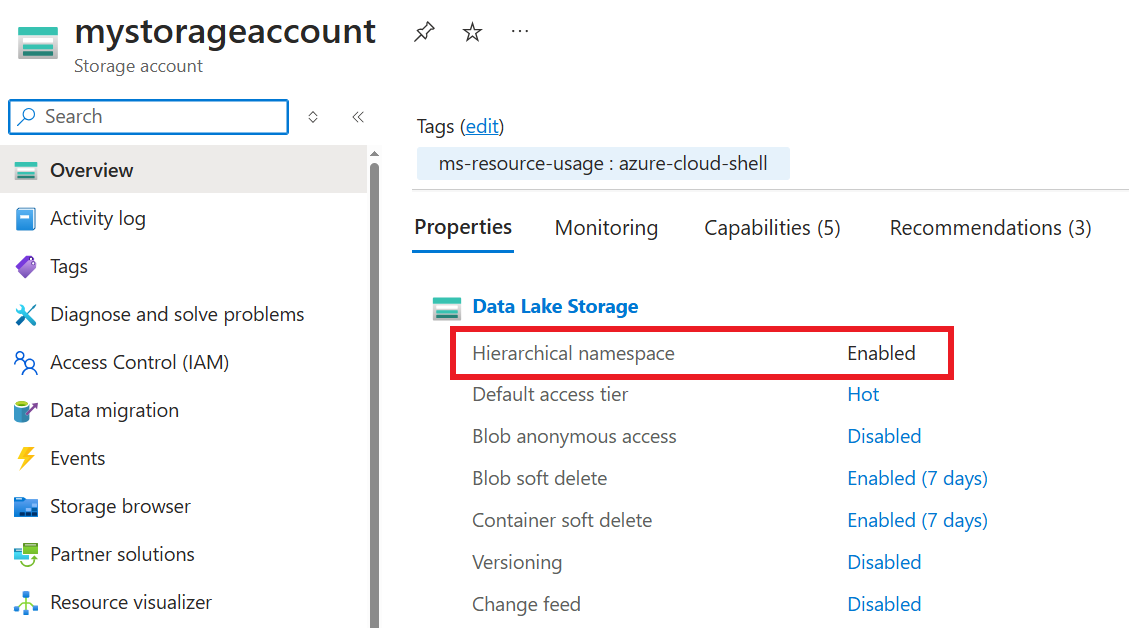
With this minimal configuration, the images container is mounted read only into /mnt/files, using access keys as the authentication method, and Block as cacheMode. The two screenshots below shows where to find container names and if hierarchical namespace is enabled or disabled.
Container names:
Hierarchical Namespace:
accessMode defines if the volume is mounted in read-only (default) or read-write mode. Valid values are:
ReadOnlyMany(default) - Volume is mounted read-only.ReadWriteMany- Volume is mounted with read-write access. Warning: This option can lead to data corruption if multiple replicas write to the same file. Read this for more information.
uid and gid defines the owning user and group for the files and directories in the mounted volume. It is optional to configure these settings, as the current version of the driver does not honor user and group ownership.
Authentication
The blob-csi-driver uses access key credentials when accessing the Azure storage account. The access key can be set manually in Radix Web Console, or it can be read by the driver from the Azure storage account using Azure workload identity if useAzureIdentity is set to true.
Access Keys
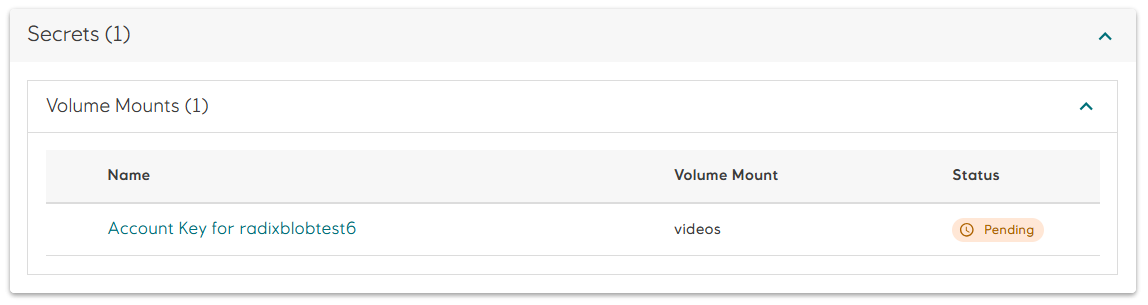
When useAzureIdentity is omitted or set to false, the access key and the name of the Azure storage account must be set manually, either on the component/job page in Radix Web Console, or with Radix CLI. Component replicas will be in Pending state until both secrets are set.
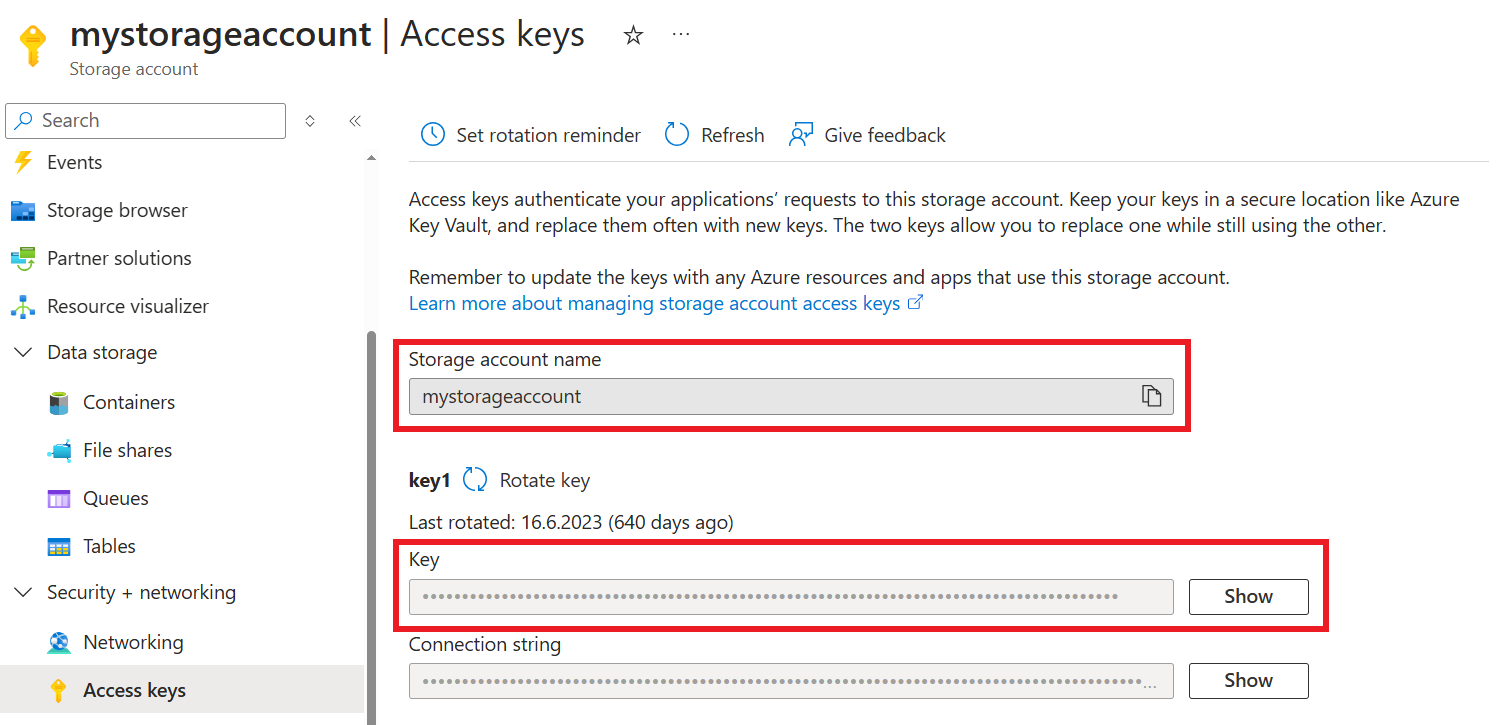
Values for these secrets is located in Access keys on the Azure storage account.
The name of the Azure storage account can also be defined in the storageAccount field in radixconfig.yaml, in which only the access key must be set i Radix Web Console.
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
container: images
useAdls: true
storageAccount: mystorageaccount # replace with real storage account name
Azure Workload Identity
When useAzureIdentity is set to true, the driver will connect to the Azure storage account using the Azure Workload Identity configured for the compopnent or job, to acquire an access key to use when accessing data in a blob container.
In order for the driver to successfully acquire an access key, the service principal configured in identity.azure.clientId must be granted the Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action permission on the Azure storage account.
The following blobFuse2 settings are required, and is used by the driver when acquiring the access key.
storageAccount- Name of the Azure storage account.resourceGroup- Name of the resource group for the storage account.subscriptionId- ID of the subscription for the storage account.
Example configuration:
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
container: images
useAdls: true
storageAccount: mystorageaccount # replace with real storage account name
resourceGroup: myresourcegroup # replace with real resource group name
subscriptionId: ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff # replace with real subscription ID
Cache Modes
Caching improves subsequent access times, and can reduce ingress and egress traffic to the Azure storage account, which in turn can lower cost related to data transfer.
cacheMode defines how data should be cached:
Block(default) - Improve performance for operations on large files by reading/writing blocks instead of entire files.File- Cache entire files for improved subsequent access.DirectIO- Disables caching.
Block Cache
With block cache, the driver reads and writes fixed size blocks of data, defined by blockSize (default 4MB), instead of the entire files. Blocks are cached by the driver in a memory pool, defined by poolSize (default 48MB), and in the OS kernel cache, on the node where the replica is running. The driver will also prefetch consecutive blocks, defined by prefetchCount (default 11), from the current position of the file. prefetchOnOpen defines if prefetching should start when the file is opened, or wait for the first read. Data operations are performed in parallel, defined by parallelism (8 threads by default).
When a file is opened and cached data exist, the driver will check if the source file has changed by comparing file attributes (Size, Modified) for the cached data, with the current attributes (see Attribute Cache) of the source file. If a change is detected, the driver will evict the cached data and fetch up-to-date data from the Azure storage account.
The driver also supports using disk a cache for data blocks. This cache has its own timeout defined by diskTimeout. Disk caching is disabled by default, and must be enabled by setting diskSize (in MB) to the desired disk cache size.
The following settings are available to fine-tune block cache:
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
container: images
cacheMode: Block
blockCache:
blockSize: 4 # Size in MB
poolSize: 48 # Size in MB
prefetchCount: 11
prefetchOnOpen: false
parallelism: 8
diskSize: 0 # Size in MB
diskTimeout: 120 # Seconds
blockSize defines the size of a block to be downloaded as a unit from the Azure storage account. Increasing this value can improved the transfer rate when reading large files.
The following table shows the transfer rate when reading a 3GB file using different values for blockSize:
| Block Size | Transfer Rate |
|---|---|
| 4 | 220 MB/s |
| 8 | 350 MB/s |
| 16 | 440 MB/s |
poolSize defines the total size of the memory pool that the driver will use for caching data blocks. The default value is set to blockSize + prefetchCount * blockSize, which is the minimum allowed value. If set to a lower value, Radix will automatically adjust it at runtime.
prefetchCount defines how many blocks the driver will prefetch at max when sequential reads are in progress. Prefetching can be disabled by setting the value to 0. Otherwise the value must be 11 (default) or higher. When only small parts of a large file needs to be read, it can be beneficial to disable prefetching to reduced network traffic from the Azure storage account.
Disk caching, enabled when diskSize is set to a non-zero value, is used by the driver to store data blocks as files on disk. The driver will check the disk cache for data blocks when reading from a file, and the requested data is found neither in the memory pool nor in the kernel cache. diskTimeout defines how long unused disk cache entries is stored on disk before being evicted.
File Cache
With file cache, the driver downloads and caches the entire file when it is opened. The cached file remains in cache for a duration defined by timeout (default 120 seconds).
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
container: images
fileCache:
timeout: 120 # Default value
Direct IO
DirectIO disables caching on driver and kernel level. All operations are sent directly to the storage account.
Attribute Cache
The attribute cache defines how long file attributes (Size, Modified) are cached by the driver. Caching is disabled by default, but can be enabled by setting timeout to a non-zero value.
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
container: images
attributeCache:
timeout: 0 # Disabled by default
Private endpoint
When requesting a private link to connect to the Azure storage account:
- in case
useAdls: false- requestSubResource: blob. - in case
useAdls: true- requestSubResource: dfs(Distributed File System).
These different sub-resources use different private link endpoint DNS zones. Read more about Azure Storage private link endpoints.
Indication that sub-resource is blob but it need to be dfs is events with failure message:
Error: failed to initialize new pipeline [failed to authenticate credentials for azstorage]
Deprecated Options
The streaming section in blobFuse2 is deprecated in favor of cacheMode. To prevent breaking changes to existing configurations, Radix will implicitly use File as cacheMode when streaming.enabled is set to false, and Block when streaming.enabled is set to true. The streaming section is ignored when cacheMode is set.
streaming will be removed in a future release, and it is therefore recommended to migrate to use cacheMode instead.
Replace implicit File cache:
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
<...>
streaming:
enabled: false
with:
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
<...>
cacheMode: File
Replace implicit Block cache:
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
<...>
streaming:
enabled: true
with:
volumeMounts:
- name: myimages
path: /mnt/files
blobFuse2:
<...>
cacheMode: Block